Le maître ignorant
Intelligence collective
Enseigner à vivre
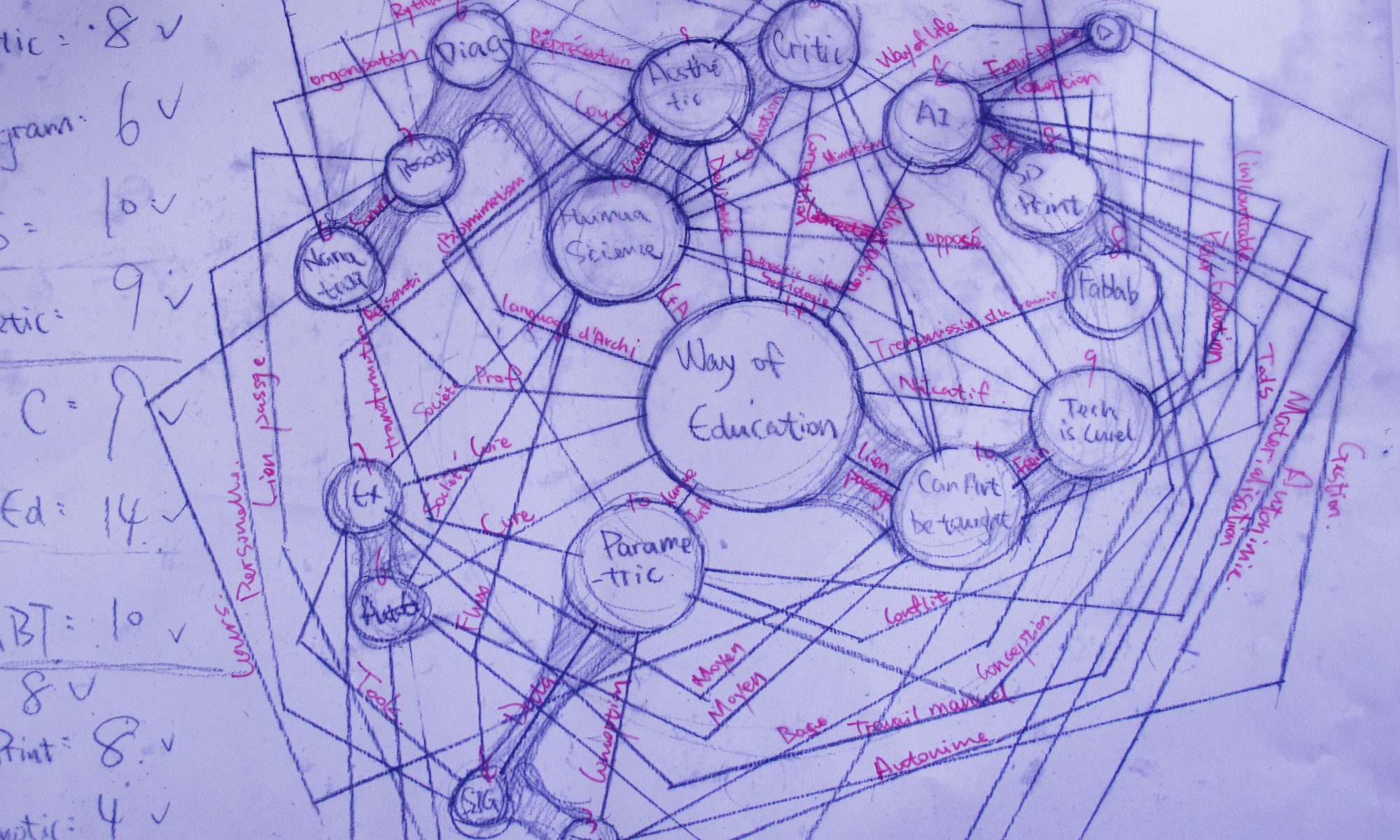
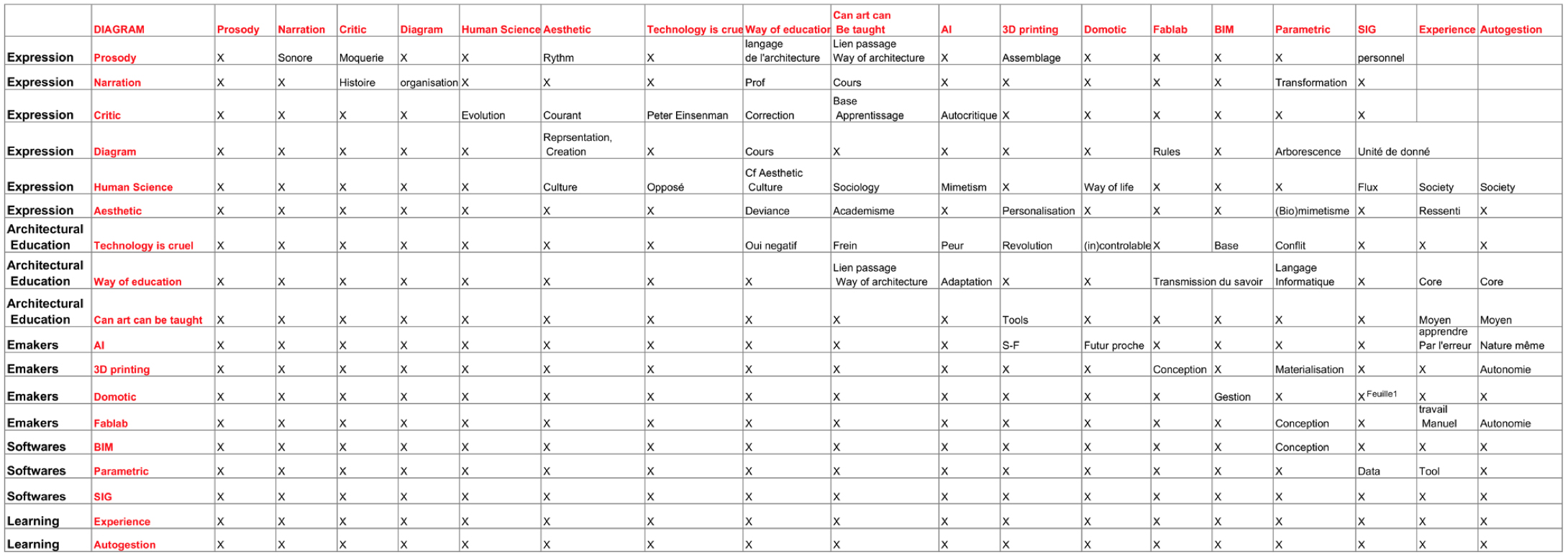
Table of the elements of the tools
E-Makers
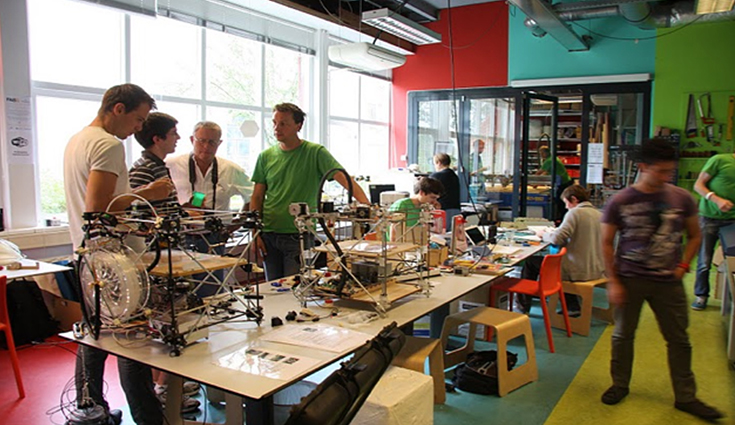
- Fablab & Culture E-Makers
FabLab (Fabrication Laboratory) are dedicated to the conception and prototyping of many different type of project. They are based on the use of numerical technology (like 3D printing…) but also on artisanal knowledge. FabLab was born in MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) around 1990. Then it was imported to France around 2000. They are open to everyone (individual, entrepre- neur, startups…) and allows the use of the differerent machines.
This work as an exchange platform of knowledge, experience, ideas. It’s working as a coworking space.
Photo of Fablab
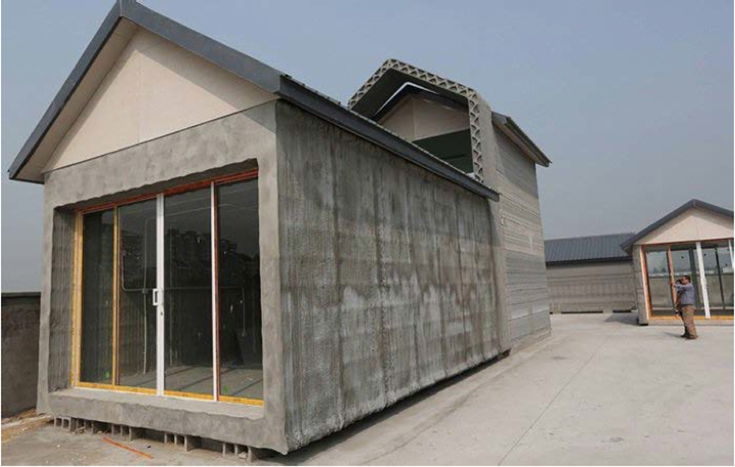
- 3D Printing House
3D printing house refers to various technologies that use 3D printing as a core method to fabricate buildings or construction components. Current machines are being integrated into automated and semi automated production lines and, because of the scale of construction, will feature elements of additive, subtractive and formative manufacturing processes, to handle material deposition at one scale and finishing at another. Because of the cost, 3D printing at construction scales demands clever design and can respond to the demands of architects and engineers for high value, high performance building components.
Photo of project » Dix maisons construites en 24h »
Education
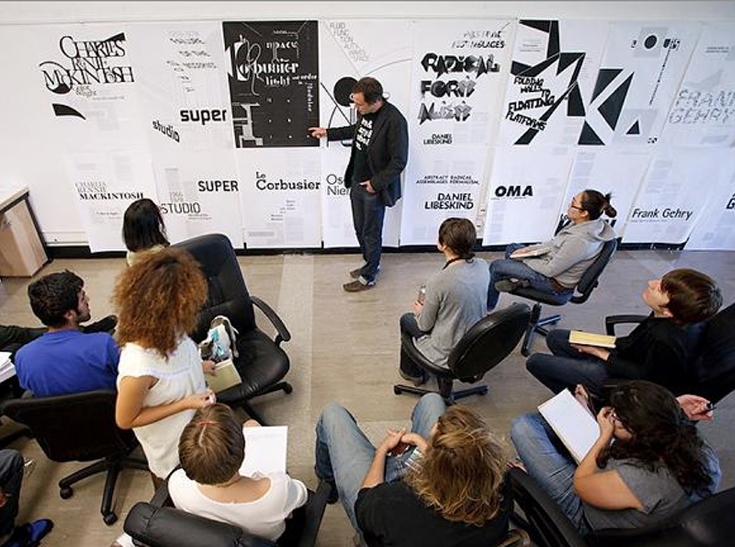
- Can architecture be taught ?
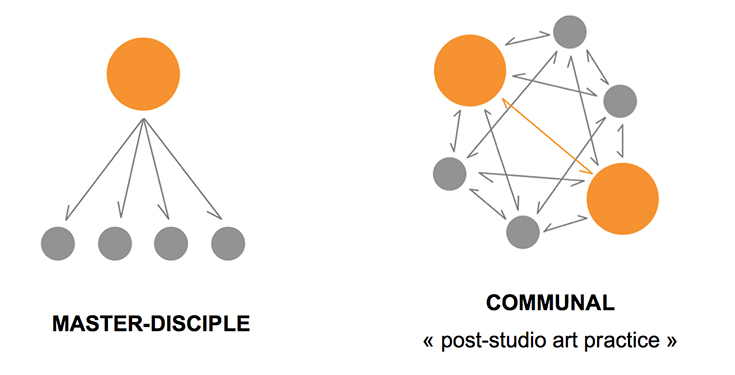
In most of art academis and in many architecture schools, the dominant pedagogical model was founded on a master-disciple relationship. Creative or technical knowledge could only be passed by the supervision of master, whose opinion was a replication of the academy’s official styles. Any challenges to this order are considered heretical.
Photo of CalArts Program
- Post-digital education
As the seminal L.A. artist, who has a studio in Santa Monica, John Baldsessari and other L.A. art educators founded CalArts program in the 1970s years, he tried to upend the current model by leading his students to the open conversation and critique about the practices of artists, that could be between student and student, students and teachers and even teachers and teachers. They think that art can not be taught, so just put the students in the environment of artists, that will free their minds to understand and to create individually. They call it post-studio art practice. It can be used in the same way in architecture.
- Technology, a cruel tool
“Technology is a cruel tool, because what it does is defer the possibility of the student being creative.It takes away from you value judgment .
Peter Eisenman
Expressing
- Narration
Action to tell, exposing a series of events in literary form -Exercise Of developing writing a story, to describe a situation, etc.
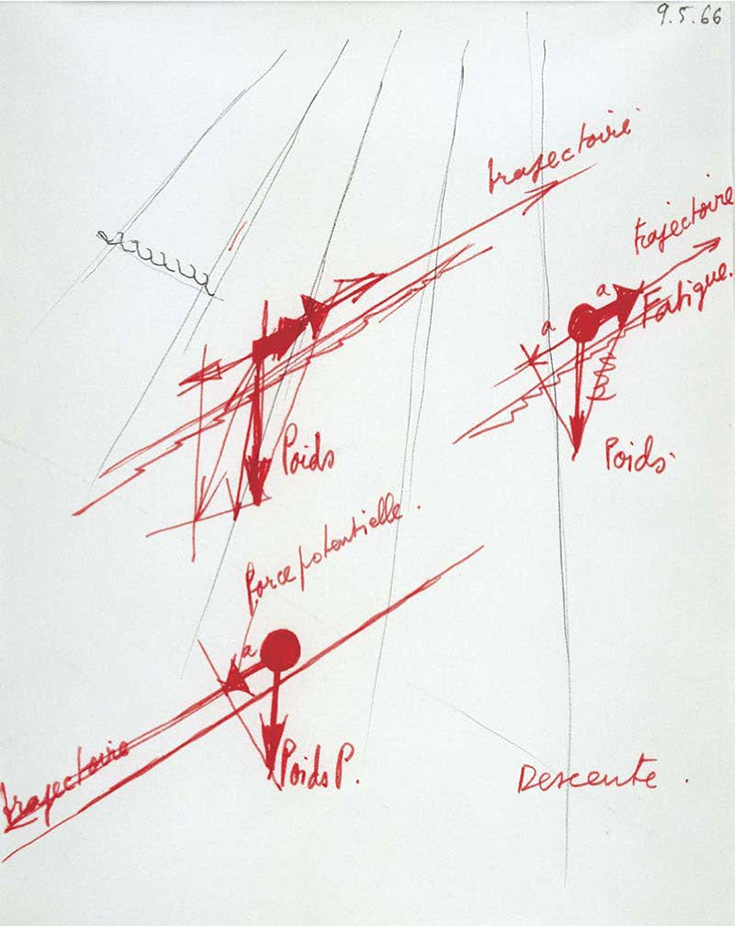
« la fin de la verticale comme axe d’élévation, la fin de l’horizontale comme plan permanent, ceci au béné ce de l’axe oblique et du plan incliné. »
Manifeste : Architecture Principe: 1966 and 1996, Paris, Septembre 1996
- Prosodie
All rules on the quantity of vowels for the composition of verse.
Set the rules for establishing a fair correspondence between the unstressed syllables or words and loud and so music time.
Study of form and substance of phonic elements whose boundaries do not coincide with those of the phoneme, whether lower (like s’mores) or above (as the syllable, the word, the phrase and sentence).
Prosodie of Architecture: Ambiences and proportions
- Human science
The study and interpretation of the experiences, activities, constructs, and artifacts associated with associated with human being.
- Critics
Professional way to communicate an assessment and an opinion of various forms of creative works.
- Aesthetic
The branch of philosophy dealing with beauty and taste.
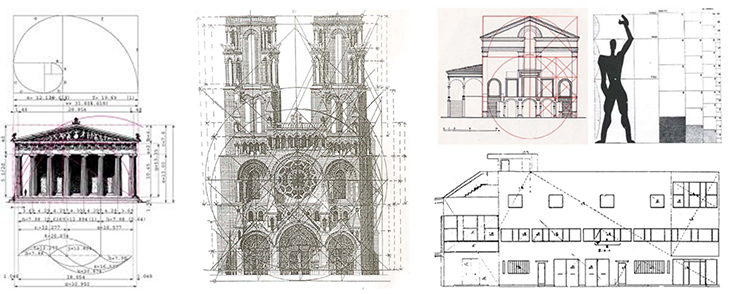
Evolution of aesthetics in architecture
- Diagram
A symbolic representation of information according to some visualization technique.
Learning
- Autogestion / Experience
Learning is the act of acquiring new, or modifying and reinforcing existing, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, or preferences and may involve synthesizing different types of information.
Learning by imitation
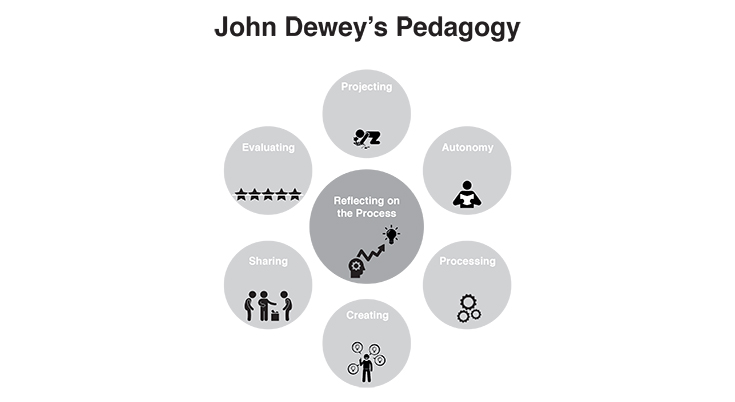
John Dewey has created the Laboratory School at the university of Chicago. For Dewey the most important is to do projects, make own experiences. He tries to learn the autonomy too.
The activity has to motivate. There is no evaluation to delete the fear to make a mistake.
John Dewey’s pedagogy
Software
- CAD
CAD = Computer aided design
Logiciel UNISURF 1966 Dassault CATIA 1977 Rhinoceros 1980 Autodesk AutoCAD 1982 Graphisoft Archi CAD 1982 Verctorworks 1985 VariCAD 1988
Reivt 2000
Grasshopper ( plug-in ) 2007
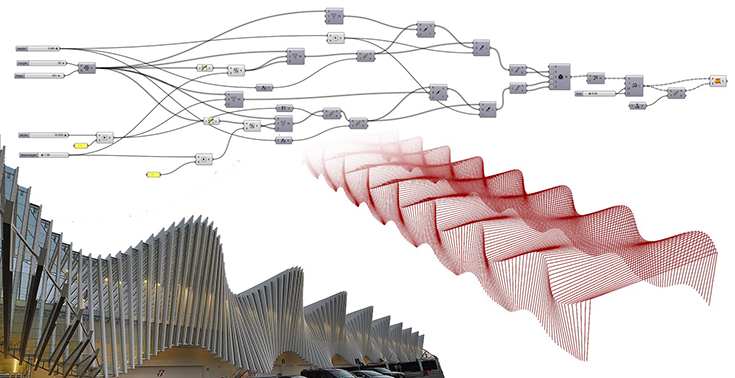
- Parametric Conception
Parametric design is a mode of operation of current computer-aided design software. This is to define an entity by parameters that can be easily changed. In this way, the definition of the part is easily changed.
Parameters can be of several types: intrinsic, Cartesian, situational.
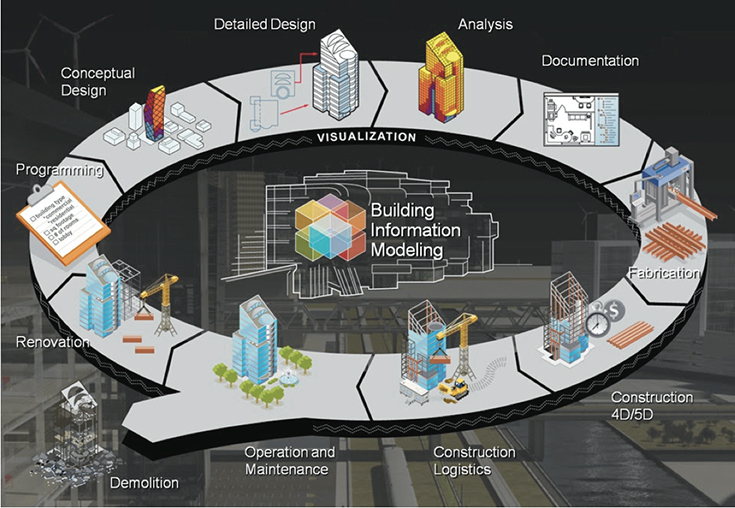
- BIM
Building Informa on Modeling (BIM) is a digital representationon of physical and functioonal characteristics of a facility. BIM is a process that involves the creation and use of an intelligent 3D model to make be er decisions about a project and communicate.